Freshwater Aquarium Care 101: Your Quick-Start Guide to Water Chemistry Success
Freshwater Aquarium Care 101: Your Quick-Start Guide to Water Chemistry Success

Whether you're a seasoned aquarist or just beginning your underwater journey, mastering water chemistry is the key to creating a thriving aquatic paradise. Don't let the science intimidate you: with the right knowledge and tools, you'll be maintaining crystal-clear, fish-friendly water like a pro! Think of water chemistry as the invisible foundation that supports your entire underwater ecosystem, and once you understand the basics, your aquatic adventure will flow smoothly.
Water chemistry might seem complex at first glance, but here's the truth: your fish live in the same water they eat and produce waste in, making water quality absolutely essential for their survival. Clear water doesn't always mean safe water: harmful chemicals can accumulate invisibly, which is why experienced aquarists often say "fishkeeping is more about keeping water than fish."
Why Water Chemistry Creates the Foundation for Success
Your mesmerizing aquatic display depends on invisible chemical processes happening 24/7. Good water quality serves as your best defense against fish stress, illness, and death while promoting vibrant plant growth and supporting the beneficial bacteria your aquarium ecosystem relies on.
Think of your aquarium as a closed-loop system where every element affects everything else. When water chemistry stays balanced, your fish swim freely with bright colors and active behavior. When it's off, even the hardiest species can struggle to survive.

The Seven Essential Parameters Every Aquarist Must Monitor
Let's dive into the critical water parameters that determine whether your underwater world thrives or merely survives:
Ammonia (NH3/NH4+): The Silent Killer
Ammonia represents the most toxic compound in your aquarium, originating from fish waste, decaying food, and dead plant matter. In acidic conditions, ammonia converts to the less toxic ammonium, but this process reverses as conditions change. Your goal? Keep ammonia levels at zero or as close as possible: there's no "safe" level of ammonia for your aquatic friends.
Nitrite (NO2-): The Dangerous Middle Ground
This intermediate compound in the nitrogen cycle is slightly less toxic than ammonia but still poses serious threats to fish health. Maintain nitrite levels below 0.2 mg/L, though zero remains your ideal target. Even small amounts can stress fish and compromise their immune systems.
Nitrate (NO3-): The Lesser Evil
The final product of your nitrogen cycle, nitrate is relatively non-toxic to fish at normal levels, though high concentrations fuel unwanted algae growth. Interestingly, the absence of nitrate can indicate your biological filter isn't functioning properly: you actually want some nitrate present as proof your system is processing waste effectively.
pH: The Balancing Act
Measuring acidity or alkalinity on a scale from 0-14 (with 7.0 being neutral), pH affects how other chemicals behave in your water. Most freshwater fish are remarkably adaptable and can tolerate stable pH levels, though specific species may have preferences. Stability matters more than perfection here.
Alkalinity (KH): Your System's Shock Absorber
Also called carbonate hardness, alkalinity measures your water's buffering capacity and should typically range between 4-8 dKH (70-140 ppm). This parameter is absolutely critical because the beneficial bacteria in your nitrogen cycle require adequate alkalinity to function properly.
General Hardness (GH): The Mineral Content
This measures total mineral content in your water. Hard water (high mineral content) typically correlates with higher pH, while soft water (low mineral content) usually means lower pH. Understanding your local water's characteristics helps you choose compatible fish species.
Dissolved Oxygen (DO): The Life Force
While not typically tested by beginners, adequate oxygen remains essential for both fish and the beneficial bacteria processing waste in your system. Proper surface agitation and circulation ensure your aquatic residents can breathe easily.

Understanding the Nitrogen Cycle: Nature's Waste Management System
The nitrogen cycle represents nature's elegant solution to waste management in aquatic environments. Here's how this fascinating process transforms dangerous waste into manageable compounds:
Step 1: Fish waste and decaying organic matter produce toxic ammonia
Step 2: Nitrosomonas bacteria convert ammonia to slightly less toxic nitrite
Step 3: Nitrobacter bacteria convert nitrite to relatively harmless nitrate
Step 4: You remove nitrate through regular water changes
The challenge? These beneficial bacteria colonies take many weeks to establish in new aquariums. You can accelerate this process with bacterial starter products, which dramatically reduce ammonia and nitrite spikes compared to traditional fishless cycling methods.
Once your cycle completes, ammonia and nitrite will consistently test at zero while nitrate gradually increases between water changes: this is exactly what you want to see!
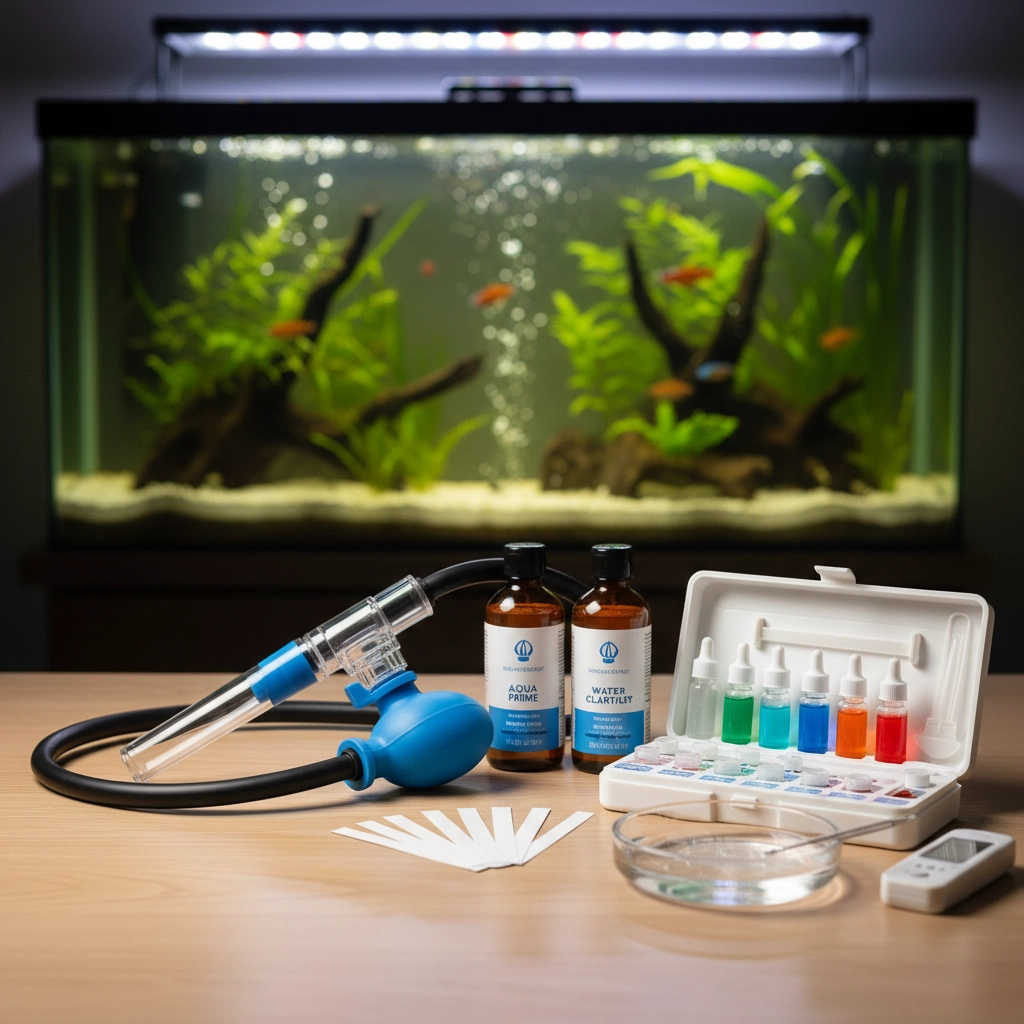
Essential Equipment for Water Chemistry Success
Water Conditioner: Your Non-Negotiable Essential
The only chemical absolutely required for any aquarium is a high-quality water conditioner (dechlorinator). This represents your bare minimum necessity: chlorine and chloramines in tap water will kill the beneficial bacteria your system depends on. Never skip this crucial step when adding fresh water to your tank.
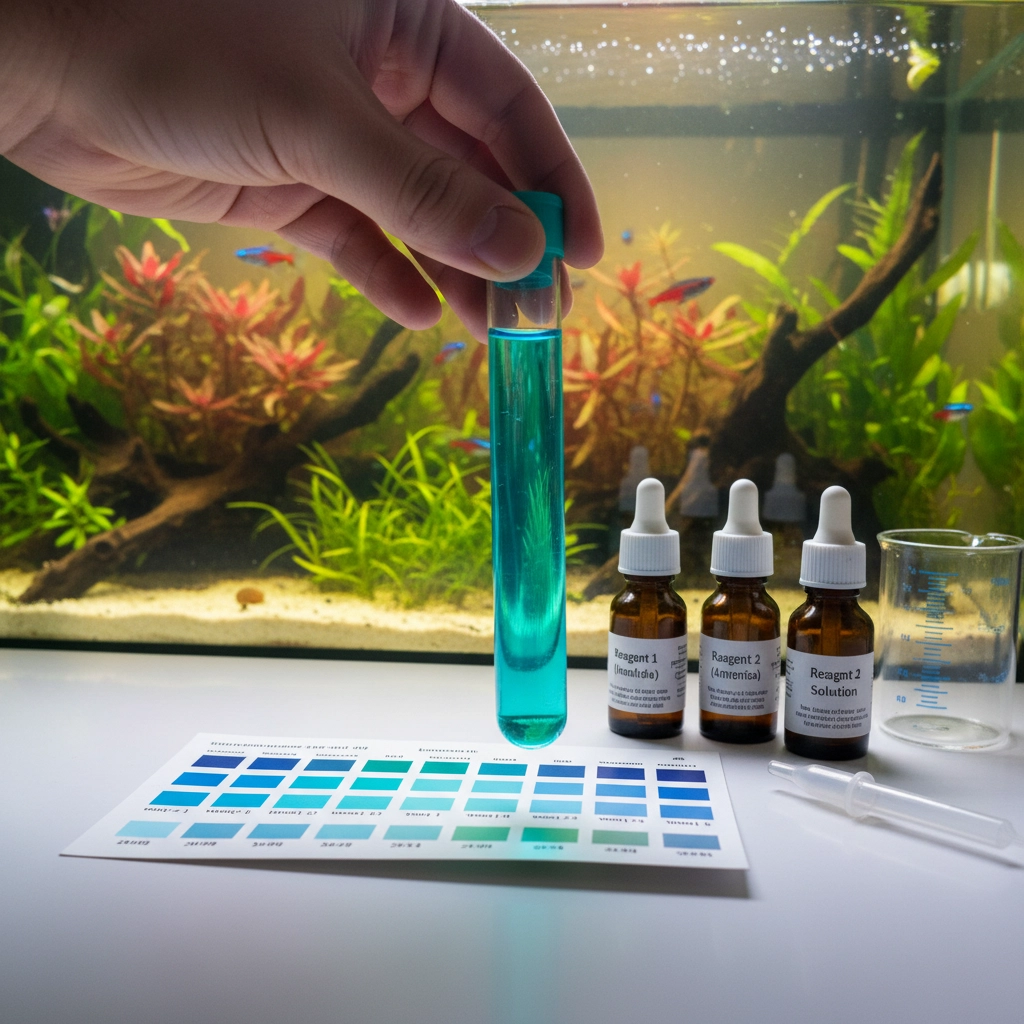
Testing Equipment: Your Crystal Ball
Invest in reliable aquarium test kits to monitor ammonia, nitrite, nitrate, and pH levels. Regular testing allows you to catch problems early and confirm your nitrogen cycle is established and functioning. Digital meters offer convenience, while test strips provide quick readings, though liquid test kits typically deliver the most accurate results.
Gravel Vacuum: Your Maintenance MVP
Essential for routine care, a quality gravel vacuum removes waste buildup that would otherwise degrade water quality. This simple tool makes the difference between a clean, healthy substrate and a waste-accumulating problem zone.

Your Maintenance Schedule for Long-Term Success
Consistency creates the foundation for thriving aquatic ecosystems. Here's your roadmap to maintaining pristine water conditions:
Weekly Protocol
Perform 25% water changes using fresh tap water treated with conditioner. This removes accumulated nitrate and waste while replenishing essential minerals. Many successful aquarists swear by this simple weekly routine as the secret to their success.
Regular Substrate Care
Combine gravel vacuuming with your water changes to prevent waste accumulation and maintain healthy substrate conditions. Focus on high-traffic areas where fish congregate and food tends to settle.
Smart Stocking and Feeding
When first establishing your aquarium, add fish gradually and feed sparingly until ammonia and nitrite levels stabilize at zero. Overfeeding ranks among the most common causes of water quality disasters: your fish need less food than you think!
The Power of Routine
Establish a maintenance schedule and stick to it religiously. Regular testing and water changes represent the twin pillars supporting every successful aquarium. Many experienced aquarists recommend testing weekly initially, then reducing frequency as your system stabilizes.
Troubleshooting Common Water Chemistry Challenges
Cloudy Water Solutions
Bacterial blooms often occur during initial setup or after major changes. Maintain your regular water change schedule and avoid overfeeding: the cloudiness typically clears as your bacterial colonies stabilize.
pH Fluctuations
Sudden pH swings stress fish more than stable levels outside their preferred range. Focus on maintaining consistent alkalinity levels, which naturally buffer pH changes.
Persistent Ammonia or Nitrite
If these toxic compounds persist after your cycle should be established, check for overcrowding, overfeeding, or inadequate filtration. Sometimes reducing bioload temporarily helps your bacterial colonies catch up.
Advanced Tips for Water Chemistry Mastery
As your confidence grows, consider these advanced strategies:
- Test at consistent times for accurate trend monitoring
- Keep a water chemistry log to identify patterns and problems early
- Learn your local tap water characteristics to anticipate seasonal changes
- Consider automated dosing systems for larger or multiple tank setups
- Understand species-specific requirements for specialized fish keeping
Creating Your Aquatic Success Story
You don't need a chemistry degree to succeed: understanding these fundamentals transforms you into a competent aquarist ready to tackle any challenge. Focus on monitoring the nitrogen cycle trio (ammonia, nitrite, nitrate), perform consistent water changes, always use water conditioner, and test regularly.
Remember: balanced, stable water chemistry matters infinitely more than achieving perfect numbers in every parameter. Your fish will reward your diligent care with vibrant colors, active behavior, and years of aquatic enjoyment.
The journey to water chemistry mastery begins with your first test kit and grows through consistent, caring attention to your underwater world. Every successful aquarist started exactly where you are now: ready to dive into the fascinating world of aquatic chemistry and create something truly spectacular.
Ready to take your aquarium care to the next level? Follow us on social media for daily tips, tricks, and inspiration from fellow aquarists! Have questions about water chemistry or want personalized advice? Don't hesitate to reach out: we love connecting with passionate fishkeepers. Share your aquarium photos with us for a chance to be featured in our thriving community of aquatic enthusiasts!






.png)


